Understanding Hydroponic pH Levels and How to Manage Them
If you’re diving into hydroponics, pH might feel like one of those intimidating, scientific things you’d rather skip. But here’s the truth: mastering pH is one of the best ways to ensure your hydroponic plants get the nutrients they need. When the pH levels are off, even a well-nourished plant can struggle to grow and thrive, and who wants that?
In this guide, we’ll break down the basics of pH in hydroponics, what it is, why it matters, and, most importantly, how you can easily manage it to keep your plants happy and healthy.
1. What Is pH in Hydroponics?
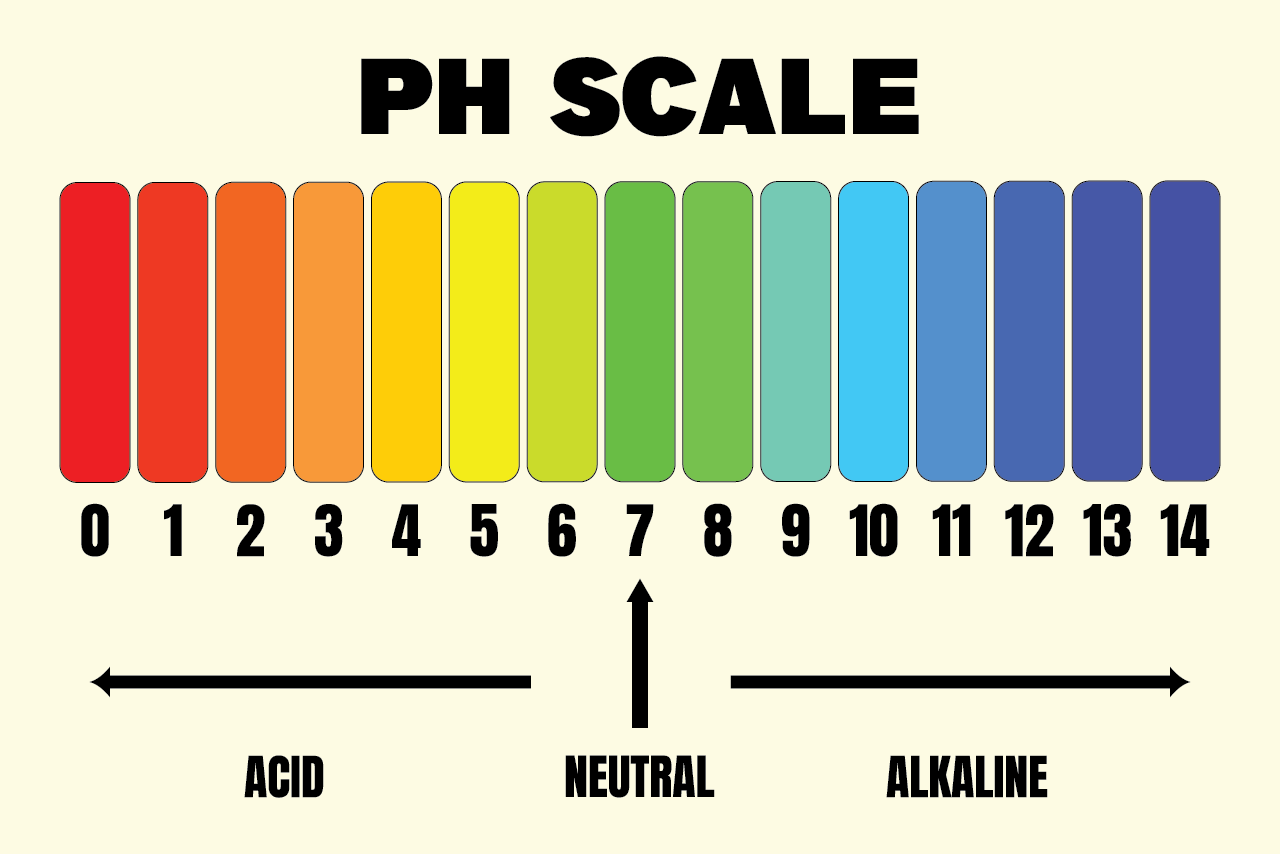
pH measures how acidic or alkaline a solution is, on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. In hydroponics, the pH of your nutrient solution determines how well your plants absorb nutrients.
- Acidic: A pH level below 7.
- Alkaline: A pH level above 7.
- Neutral: A pH level of 7.
For hydroponics, most plants thrive in a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. This slightly acidic range allows essential nutrients, like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, to dissolve effectively in water, making them available for the plant roots.
2. Why pH Levels Matter in Hydroponics
In a traditional soil garden, soil acts as a buffer, helping to stabilize pH levels. However, in a hydroponic system, plants rely solely on the water-based nutrient solution, so the pH directly affects nutrient availability. If pH levels are too high or too low, plants can suffer from nutrient deficiencies or toxicity, which leads to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced yields.
Common issues with improper pH levels:
- High pH: Nutrients like iron, manganese, and phosphorus become less available.
- Low pH: Calcium, magnesium, and molybdenum absorption can be hindered.
Pro Tip: Regularly monitoring and adjusting your pH levels helps prevent these issues and keeps your plants in optimal growing conditions.
pH management starts with the right setup. Read more in Hydroponics Systems Explained: A Beginner’s Guide to help you establish a balanced system.
3. Tools for Testing pH Levels
Testing pH levels is simple with the right tools. Here are a few options:
- pH Test Strips: Affordable and easy to use, pH test strips change color based on pH level. However, they may lack the precision needed for hydroponics.
- Liquid pH Test Kits: These kits involve adding a few drops of test solution to a water sample, which changes color to indicate the pH. They’re accurate and more precise than strips.
- Digital pH Meter: A digital meter provides quick, accurate readings, making it a top choice for hydroponics. You’ll need to calibrate it occasionally and keep the probe clean for best results.
Pro Tip: For digital meters, keep the probe stored in a pH storage solution to maintain accuracy.
4. How to Adjust pH Levels in Hydroponics
Once you’ve tested your nutrient solution, you may need to adjust the pH level to keep it in the ideal range.
To Lower pH:
- pH Down Solution: Commercial pH down solutions typically contain phosphoric acid, which safely lowers pH.
- Vinegar or Lemon Juice: These household items can lower pH in a pinch, but they’re not as stable as commercial solutions and may require more frequent monitoring.
To Raise pH:
- pH Up Solution: Potassium hydroxide-based pH up solutions work well for raising pH.
- Baking Soda: Baking soda can raise pH, though it’s less stable than commercial products and can lead to sodium buildup if used excessively.
Pro Tip: Add pH adjusters in small increments, allowing the solution to circulate before retesting. This helps prevent drastic swings in pH.
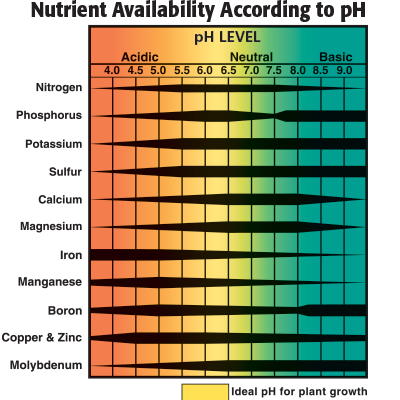
5. Nutrient Availability and pH
One of the key reasons pH is so crucial in hydroponics is that it directly impacts nutrient availability. Plants rely on specific pH levels to access essential nutrients in the water. For instance, in a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5, plants can absorb nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and trace minerals like iron and zinc effectively. When the pH drifts outside this range, nutrient absorption can become blocked or imbalanced.
Related: How to Choose the Best Hydroponic Nutrients for Your Garden
For example, if the pH becomes too high, nutrients like iron and manganese become less available, leading to deficiency symptoms like yellowing leaves or stunted growth. Likewise, a low pH can restrict access to calcium and magnesium, causing plants to struggle with growth and development. Keeping pH levels steady within the ideal range ensures your plants can absorb a balanced diet of nutrients, promoting healthier growth and stronger yields.
6. Tips for Maintaining Stable pH Levels
Keeping pH stable over time is easier when you’re proactive about it. Here are a few tips to help:
- Check pH Regularly: Make it a habit to check pH daily, especially when setting up a new system or changing nutrients.
- Use Quality Nutrients: High-quality hydroponic nutrients are formulated to dissolve easily in water and maintain a stable pH range.
- Monitor Water Temperature: Warmer water can impact pH stability and reduce oxygen levels, leading to root stress.
- Clean Your System Regularly: Organic matter buildup in the reservoir can impact pH, so regular cleaning helps maintain a stable environment.
Pro Tip: Use a buffer solution designed for hydroponics if you find pH fluctuating often. Buffer solutions help stabilize pH by neutralizing acids and bases in the water.
7. Troubleshooting pH Issues in Hydroponics
Even with careful management, pH levels can sometimes drift. Here’s a quick guide to troubleshooting common pH issues:
- Frequent pH Drops: If pH drops frequently, check for root rot or algae buildup, which can acidify the nutrient solution. Cleaning your reservoir and roots can help.
- pH Rises Rapidly: Hard water with high mineral content can cause pH to rise. Using filtered or distilled water can help prevent this.
- pH Unstable After Nutrient Addition: Some nutrients may cause pH shifts. Mixing nutrients in the right order (e.g., add calcium first, then phosphorus and nitrogen sources) can help stabilize pH.
Pro Tip: Keep a pH log to track any patterns or issues. Noting changes can help you spot trends and prevent future problems.
Struggling with pH issues? You might find some helpful tips in Common Hydroponic Mistakes Beginners Make and How to Avoid Them to troubleshoot and prevent these issues.
Conclusion
Managing pH levels in hydroponics might sound technical, but once you understand the basics, it’s straightforward and worth the effort. By keeping pH in the ideal range, you’re setting your plants up for better nutrient absorption, faster growth, and a stronger yield.
Start by testing regularly, adjusting carefully, and using high-quality nutrients. With these tips, you’ll be well on your way to creating a balanced, thriving hydroponic system! Happy Gardening!